With products like the Ryzen 7 5800X3D earning the crown as the best CPU for gaming, you’re probably wondering what CPU cache is and why it’s such a big deal in the first place. We already know that AMD’s upcoming Ryzen 7000 CPUs and Intel’s 13th-generation Raptor Lake processors will focus on more cache, signaling this will be a critical spec in the future.
Contents
- What is CPU cache?
- How does cache work?
- Does CPU cache matter for gaming?
But should you care about CPU cache? We’re going to break down what CPU cache is, why it’s so important, and how it can make a massive difference if you’re gaming.
Recommended Videos
What is CPU cache?
Cache is the amount of memory that is within the CPU itself, either integrated into individual cores or shared between some or all cores. It’s a small bit of dedicated memory that lives directly on the processor so that your CPU doesn’t need to fetch information from your system RAM every time you want to do something on your PC. Every processor has a small amount of cache, with smaller CPUs getting perhaps just a few kilobytes while large CPUs can have many megabytes worth of cache.
Get your weekly teardown of the tech behind PC gaming
Check your inbox!
But you might be wondering why cache is necessary at all when we have RAM, especially when a single stick of RAM can have several gigabytes of memory. It’s all about performance. In the 1990s, the pace of performance improvements between CPUs and RAM started to become apparent. After all, CPU designers were focused on increasing speed, while RAM designers wanted to increase capacity and neglected speed. For the CPU designers, this was a problem because RAM speed is a crucial factor in CPU performance for many applications, and the bigger the CPU-RAM gap got, the harder it would be to improve performance.
Cache was the solution. Although cache has little capacity compared to RAM, its high speed makes up for it in most cases. Cache isn’t perfect, however. Its main weakness is size; cache is physically large for how little it can store. Cache is also resilient to node shrinks, so while the cores and other components in a CPU can shrink quite easily from one generation to another, cache shrinks much less. This makes cache a very expensive component of a CPU, which is one of the main reasons why cache usually has such a small amount of storage.
How does cache work?
The mainstream adoption of cache resulted in more nuanced implementations of cache and RAM until we ended up with the memory hierarchy, with cache at the top, RAM in the middle, and storage at the bottom. This tiered approach allows critical data for the CPU to be physically closer to the processor, reducing latency and helping your PC feel snappy.
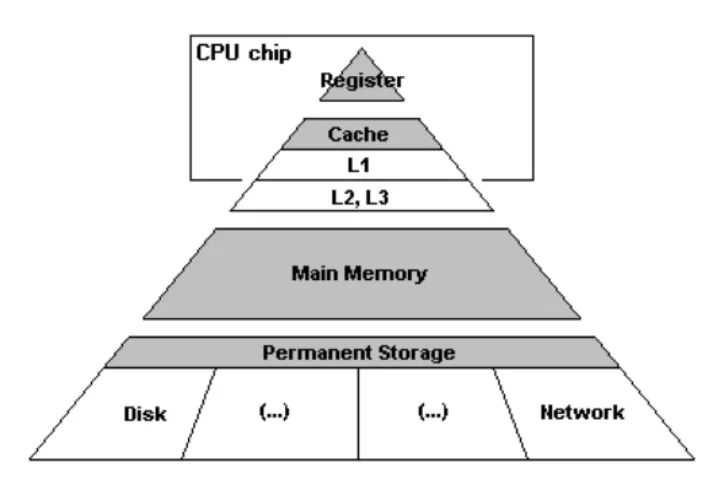
Cache has its own hierarchy, or cache levels, which are split into L1, L2, and L3 cache. These are all kinds of cache, but they perform slightly different functions.
L1 cache is the first level of cache and also the smallest, usually divided into L1 instruction or L1i and L1 data or L1d. Each core within a CPU has its exclusive chunk of L1 cache, which is usually only a few kilobytes large. The kind of data stored in L1 cache is stuff that the CPU just used or expects to use imminently. If the CPU needs data that isn’t in the L1 cache, it goes to the next level: L2.
Like L1 cache, L2 cache is often exclusive to a single CPU core, but in some CPUs, it’s shared between multiple cores. It’s also much, much larger; for example, each P-core in the Core i9-12900K has 80 kilobytes of L1 cache, as well as 1.25 megabytes of L2 cache, nearly 16 times as much. However, larger caches have higher latency, which means it takes more time for communication to happen between the CPU core and the cache. When CPUs want to accomplish things in a matter of microseconds or even nanoseconds, the slightly higher latency of L2 cache does matter. If a CPU can’t find requested data within L2 cache, it asks the next level: L3.
L3 cache is a big deal: it’s shared between some or all cores within a CPU, and it’s big. The 12900K has 30MB of L3 cache, for example, 24 times the amount of L2 cache. The latency of L3 cache is even worse than L2, but having a large L3 cache is really important to prevent the CPU from needing to ask the RAM for needed data. Except for storage, RAM has the worst speed and latency in the memory hierarchy, and whenever the CPU needs to access the RAM for required data, things grind to a halt. Ideally, anything important is going to be stored at least within L3 cache to prevent a massive slowdown.
Some CPUs even have L4 cache, but it usually functions as RAM that’s on the CPU package. Some of Intel’s first 14nm CPUs based on the Broadwell architecture included 128MB of embedded DRAM, and the company’s upcoming Sapphire Rapids server CPUs can come with HBM2, which is kind of used like an extra level of cache.
Does CPU cache matter for gaming?
CPU cache makes a big difference for gaming. Although single-threaded performance, instructions per clock (IPC), and clock speed have traditionally been said to be the most important factors in gaming performance, it’s become very clear that cache is probably the most important factor of all in the rivalry between AMD and Intel.
Cache is so important for gaming because of how games are designed today. Modern games have a lot of randomness, which means that the CPU constantly needs to execute simple instructions. Without enough cache, your graphics card is forced to wait on your CPU as the instructions pile up and cause a bottleneck. You can see an example of how much of a difference that makes with AMD’s 3D V-Cache technology in Far Cry 6below.
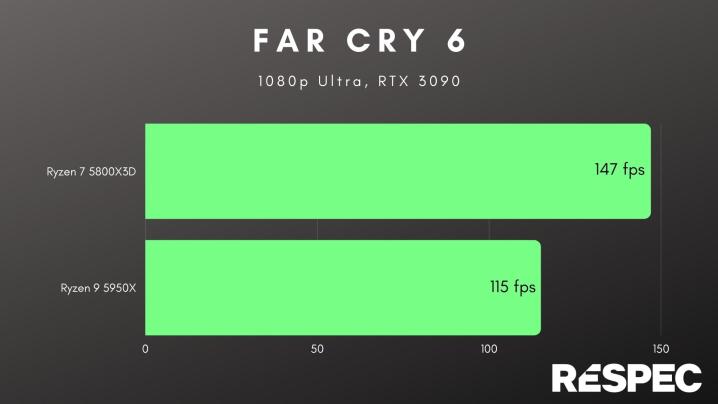
We’ve seen a trend toward more cache for gaming in recent years. AMD’s Ryzen 3000 CPUs had twice as much L3 cache as the previous generation and were much faster for gaming, almost catching up to Intel. When Ryzen 5000 launched, AMD didn’t add more cache, but it did unify the two blocks of L3 cache within the CPU, which greatly reduced the latency and put AMD in the lead for gaming performance. AMD doubled down with its 3D V-Cache technology on the Ryzen 7 5800X3D, which stacks a 64MB chip of L3 cache on top of the CPU for a total of 96MB, more than even the flagship Ryzen 9 5950X.
Intel has been playing catch-up with AMD, and its current-generation Alder Lake CPUs have up to 30MB of L3 cache, which is significantly less than most Ryzen CPUs, but they also have lots more L1 and L2 cache. However, Intel’s disadvantage in L3 capacity doesn’t mean Ryzen 5000 CPUs are much faster for gaming. In our Core i9-12900K review, we found that the 12900K was tied with the Ryzen 9 5950X for gaming performance.
The race for cache will almost certainly continue with the upcoming Ryzen 7000 and Raptor Lake CPUs. Ryzen 7000 is confirmed to have twice the L2 cache of Ryzen 5000, and we will probably see more CPUs using V-Cache. Meanwhile, Intel doesn’t have its own version of V-Cache, but Raptor Lake is rumored to have much more L3 cache than Alder Lake, just in the CPU itself.
Editors' Recommendations
- The Asus ROG Ally just got a game-changing update
- The best budget CPUs you can buy in 2024
- 9 best processors for PC gaming: tested and reviewed
- It just became the perfect time to buy a last-gen Intel CPU
- I tested Intel’s XeSS against AMD FSR — and the results speak for themselves